FAQs
Serial Port
The BB-400, an Industrial Raspberry Pi based Controller, features a single fully configurable serial port (Grey Terminal Block), capable of being set to use 1 of 3 serial communication protocols (RS232, RS422 and RS485). Serial communication involves sending data via data bits, one after another, over a single channel, from a sender or transmitter to a receiver.
The data is usually sent in binary or text (ASCII) format. Data bits are sent with a predefined frequency; the baud rate. Both the transmitter and receiver (both ends of the serial link) must be configured to use the same bit frequency. The transmitter and receiver must use the same overall configuration, including stop bits and flow control. Otherwise, the data may be misinterpreted, or not recognised at all.
The BB-400 serial port is capable of accepting all the most common baud rates, the minimum being 300, and the maximum 921,600.
For more information on the difference between RS232, RS422 and RS485 serial communication, please see following: Difference between RS232, RS422, and RS485 serial communication
Serial jumpers
The serial port has 4 configuration jumpers located on the inside of the case. They must be set based on the serial mode, RS232, RS422 or RS485.
- FT (Full Duplex Termination)
- HT (Half Duplex Termination)
- B+ (Biasing)
- B- (Biasing)
To find out more about the differences between Full Termination and Half Termination please see the following: Difference between Full termination, Half termination, and Biasing resistors
Keeping Serial Jumpers in Park Mode
By default, the BB-400 is configured to RS232 serial communication protocols. It is possible to use RS422 and RS485 communication with the jumpers in park mode, but there are limitations. As data rates and/or cable lengths increase, termination becomes mandatory.
- Termination resistors provide an impedance at each end of the cable which matches the impedance of the cable. These prevent signals being reflected back down the cable which would cause interference.
- Biasing resistors put the transmission line in a known good state when it is not driven by a transmitter. This means any receivers will not receive noise, and interpret it as a valid signal.
Below is the configuration for park mode:
| Jumper Configuration (Park mode) |
|---|
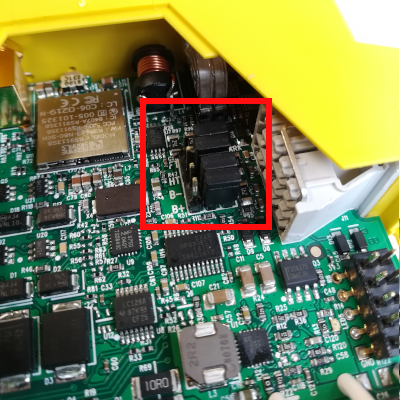 |
Changing to Full Duplex mode or Half Duplex mode
Configuring the BB-400 into Full Duplex or Half Duplex is simple. Place the resistors into the specific configuration shown below.
Full Duplex (FD) Configuration and Half Duplex (HD) Configuration:
| Jumper Configuration (FD mode) | Jumper Configuration (HD mode) | |
|---|---|---|
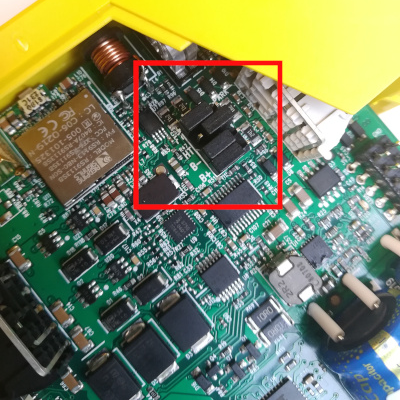 |
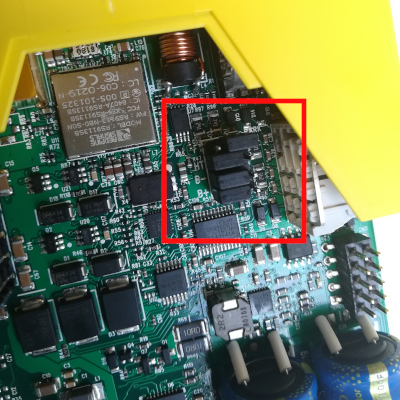 |
To find out more about Full-Duplex mode or Half-Duplex mode and in which circumstances they should be used, please see the following link: What is the difference between Full termination, Half termination, and Biasing resistors
Related FAQs
- How do I configure the BB-400’s Serial Port Jumpers?
- How do I send serial data straight to the cloud?
- How do I use the BB-400’s Serial Port in Node-RED?
- How to open, send data, and close serial Port on BB-400
- Is Serial tunnelling suitable for my application?
- RS232, RS422 & RS485 Standards
- What is the difference between Full Termination, Half Termination and Biasing resistors?
- What is the difference between RS422 communication and RS485 communication?
